Describe the Structure of the Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated retroperitoneally in the pelvic cavity posterior to the pubic symphysis. It plays two main roles.

What Are The Major Structures Of The Urinary System Quora
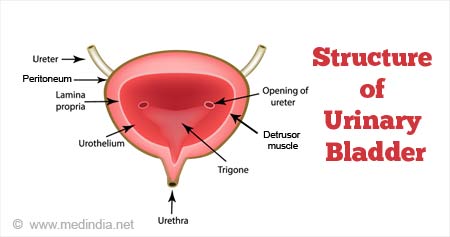
1-3 The inside of the bladder is lined with a thin layer of cells which is called the urothelium.
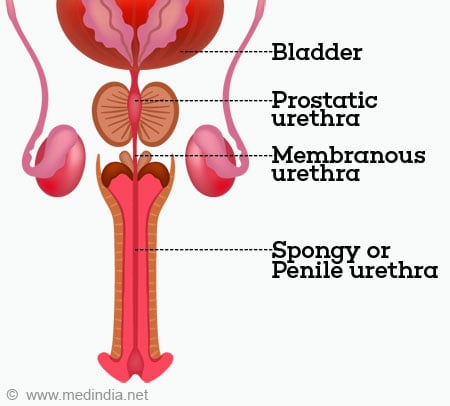
. Kidney Ureter Two of these transport urine Structure that passes urine out of the body Site of urine production Site of urine storage Bladder Urethra. Collected urine and funnel to the pelvis. The transitional epithelium layer is the first layer on the inside of the bladder.
The elementary structure of the ureter is elastic muscles entangled in fiber layers that allow to control the sphincter. It has a folded internal lining known as rugae which allows it to accommodate up. The urinary system is also known as the renal system.
The urinary bladder consists of different layers of tissue. Functions of the lower urinary tract to store and periodically eliminate urine are regulated by a complex neural control system in the brain spinal cord and peripheral autonomic ganglia that coordinates the activity of smooth and striated muscles of the. In females the main urethra functions are the transportation of urine out of the body prevention of urine reflux and protection against pathogenic bacteriaIn males the urethra has four functions the expulsion of urine the expulsion of sperm the prevention of either of these fluids from traveling back into the lower.
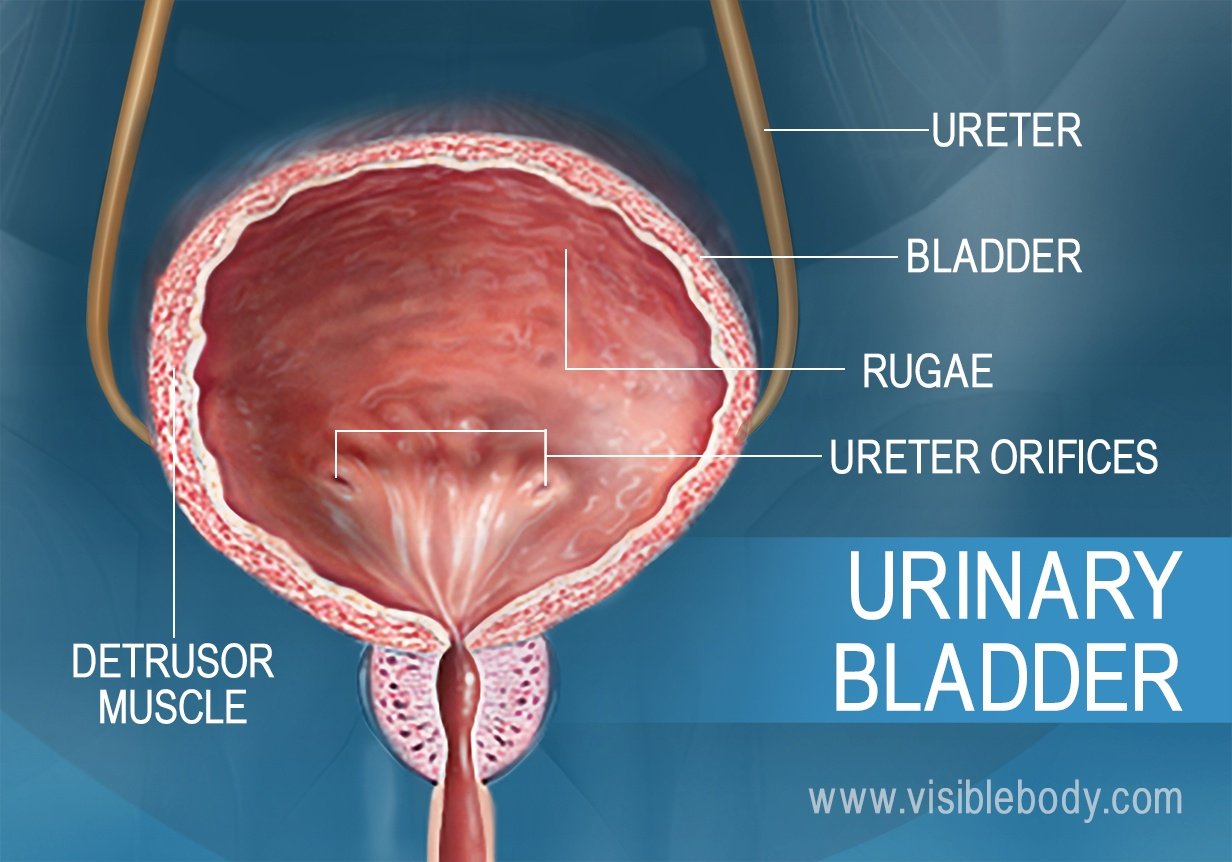
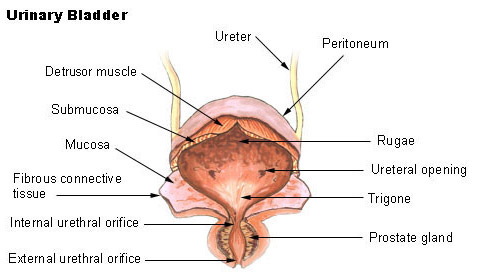
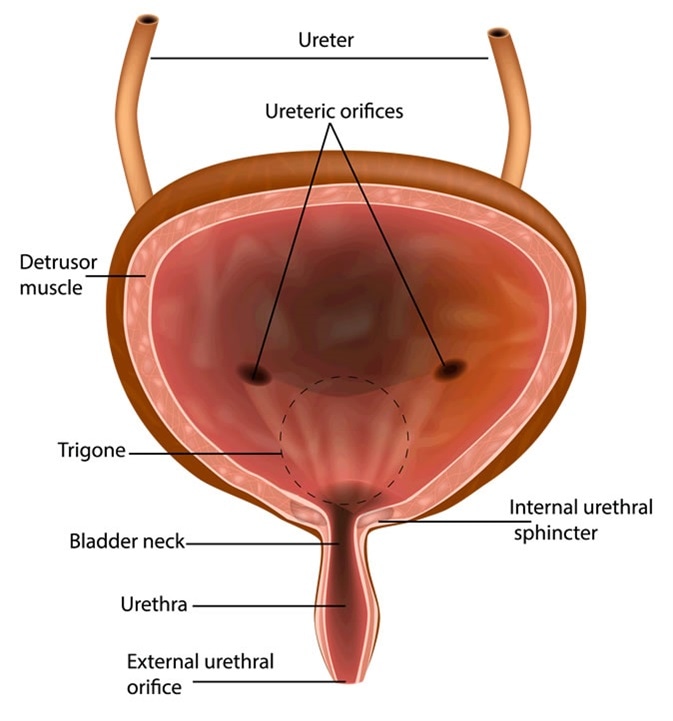
Muscular wall of the urinary bladder that surrounds the neck of the bladder and forms an internal urethral sphincter. Each kidney consists of millions of functional units called Nephrons. Structure - distensible organ that is hollow and muscular.
The kidneys produce urine by filtering excess water from our blood. This tissue also protects the bladder from alkaline or acidic urine. The tube from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Papillary ducts drain through renal papillae - minormajor calyces - renal pelvis - out the ureter - urinary bladder - urethra. Mucosa layer forms the innermost layer lining the hollow organ. Location - within the pelvic cavity posterior to the symphasis pubis and inferior to the parietal peritoneum.
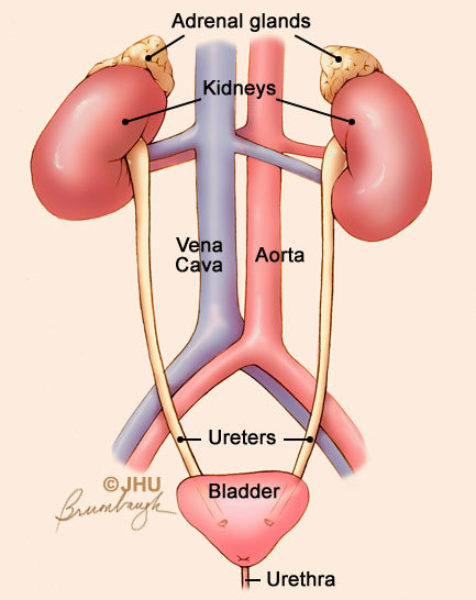
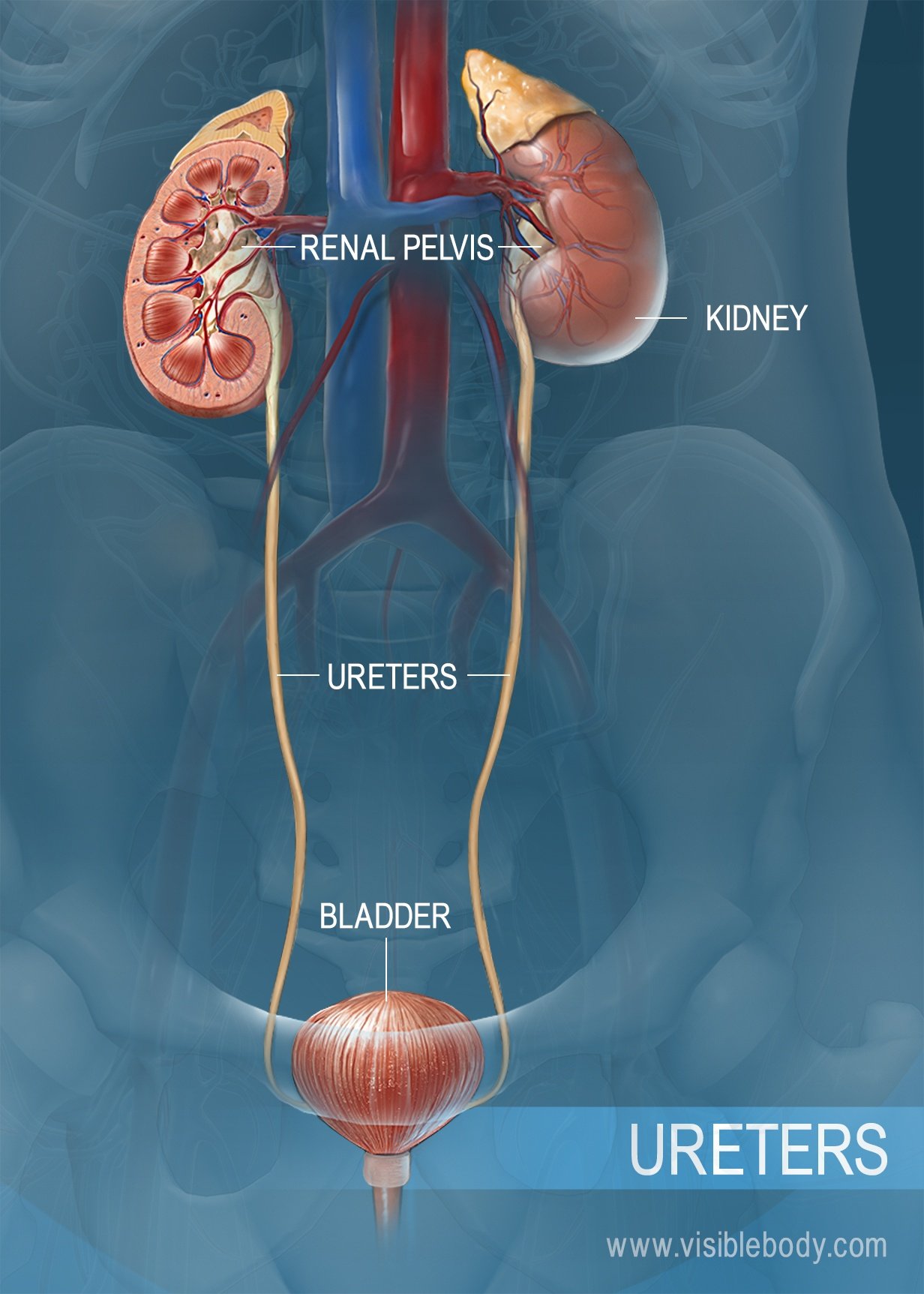
In the kidneys and flows through the ureters to the urinary bladder which stores urine until t is eliminated from the body through the urethra KIDNEY bean shaped retro peritonealeither of two bean-shaped excretory organs that filter wastes especially urea from the blood and excrete them and water in urine. Name every gross or microscopic structure it passes through on its journey. Between this lining of cells the urothelium and the muscles of the bladder is another very thin layer of tissue called the lamina propria.
Ans Structure of Urinary system. Match the labels with the structure of the urinary system they describe. Glomerulus- Bowmans Capsule- proximal convoluted tubule- descending loop of henle- asending loop of henle-distal convoluted tubule- collecting tubule- calcyx- renal papilla- renal pelvis- ureter- bladder- urethra.
Structure of the Bladder. It is a freely movable. This acts as a lining that.
The mucosa lining the urinary bladder is additionally lined with transitional epithelial tissue that can stretch to store large volumes of urine. Funnel shaped structure at the apex of pyramids into the renal pelvis Trace the flow of urine out of the body beginning with the papillary ducts. The bladder divideS into two main parts each with its own features.
3 rows Key facts about the urinary bladder and urethra. Structure of the Bladder when Expanding. Unlike the female urethra the male urethra is a structure shared between the urinary and reproductive systems.
The upper part above the ureteric orifices is composed of the apex and body while the lower part is composed of the fundus trigone and neck. 1Mucosanumerous folds 2Muscular layer has 3 distinctives layers of smooth muscle. The bladder is an organ of the urinary system.
Match the labels with the structure of the urinary system they describe. A hollow organ. The muscular layers cover the whole path between the kidney to the bladder.
The blood transports the debris to the kidneys. Features and Structure of the Bladder. The capacity of the bladder is.
The male urethra extends from the bladder passing through the prostate gland of the reproductive system immediately inferior to the bladder before passing below the pubic symphysis see Figure 1b. View the full answer. The bladder walls are mainly made up of muscle tissue but the inside of the bladder is lined with two different types of tissue.
Triangular area at the base of the bladder made up of the openings from the ureters and the opening into the urethra. The urethra is a tube which extends from the urinary bladder and opens outside the body and it allows the urine to pass outside the body. What are the basic layers that form the structure of the urinary bladder.
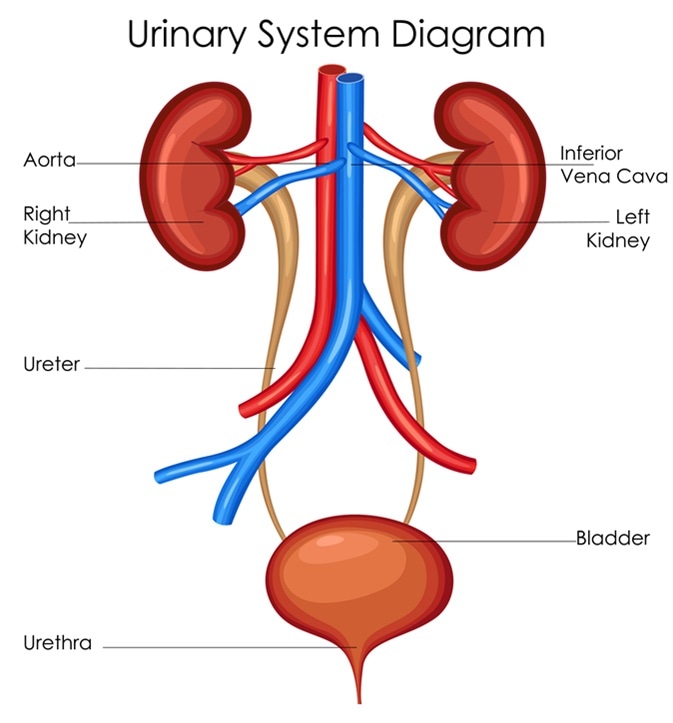
The urinary system consists of the kidneys ureters urinary bladder and the urethra. Urethra Function and Structure. The urinary bladder is a balloon-like sac that receives the urine from the two ureters It stores the urine temporary until it is released outside the body through the urethra.
Temporary storage of urine the bladder is a hollow organ with distensible walls. Biology questions and answers.
Which Organ System Consists Of The Kidneys Ureters Urinary Bladder And Urethra Quora

Anatomical Structure Of The Urinary Bladder Vector Image

Urine Transport And Other Structures Of The Urinary System Anatomy And Physiology

Anatomy And Normal Microbiota Of The Urogenital Tract Microbiology
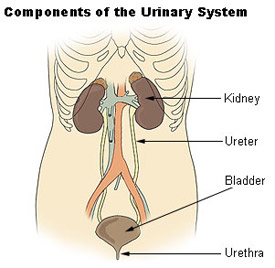
Seer Training Components Of The Urinary System

What Are The Major Structures Of The Urinary System Quora

What Are The Major Structures Of The Urinary System Quora
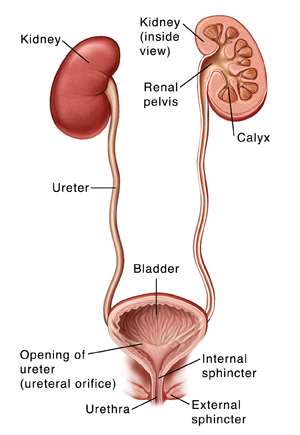
Anatomy Of The Pediatric Urinary Tract Saint Luke S Health System
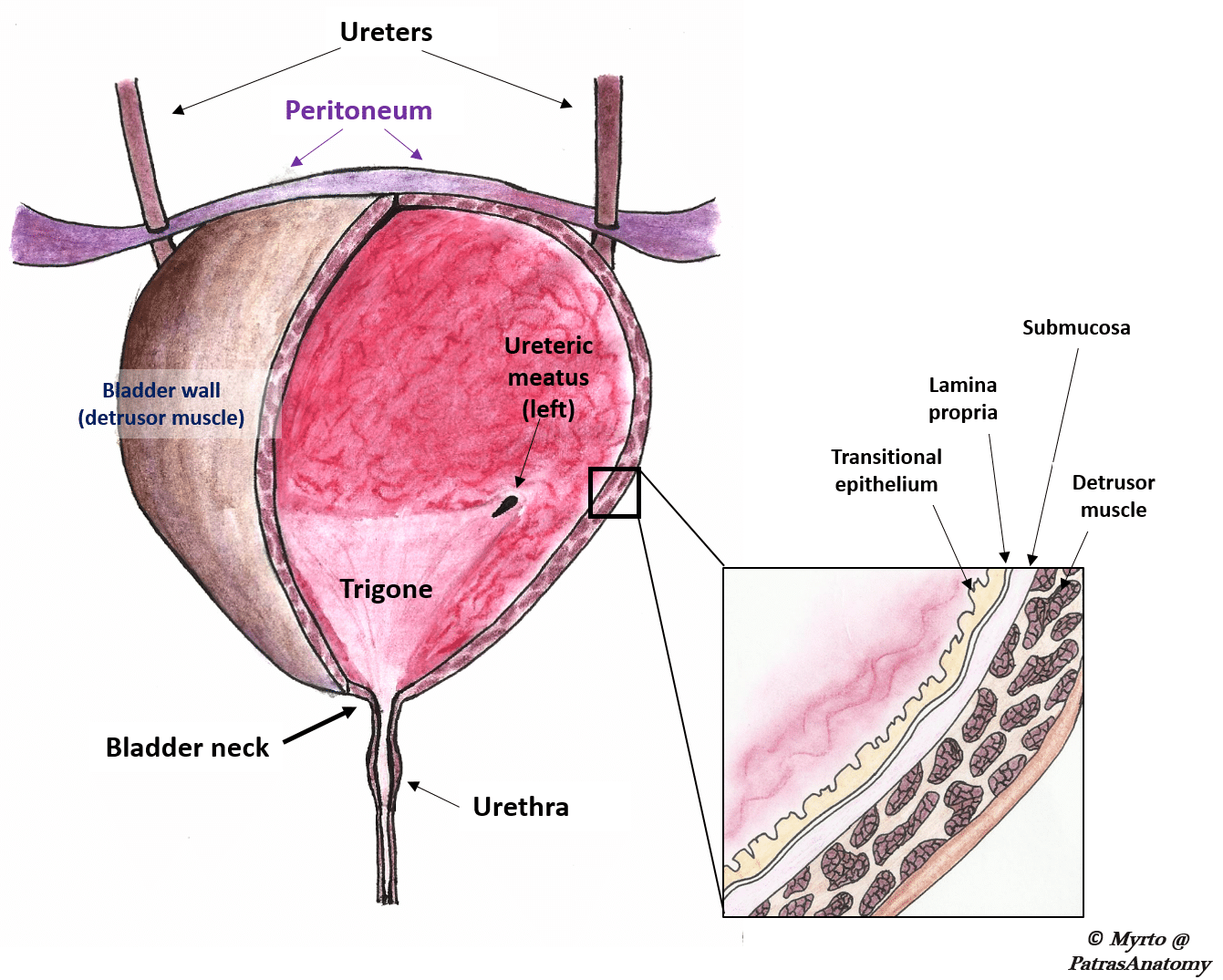
The Urinary Bladder Structure Function Nerves Teachmeanatomy
Bladder Diverticulum Causes Symptoms Diagnosis And Management

Urinary System Diagram How To Draw Labelled Diagram Of Urin System W Human Cell Diagram Diagnostic Medical Sonography Student Diagnostic Medical Sonography
Overview Of The Bladder Bladder Cancer Johns Hopkins Pathology

Comments
Post a Comment